On this page
This web page will help parents, students and the community to understand STEM teaching and learning from preschool to year 12. For parents and caregivers, find out about how you can support STEM learning at home. For students, discover the broad range of STEM study and career pathways that match your skills and interests. For industry, find out how you can be part of upskilling the next generation of STEM talent.
Explore STEM
What is STEM learning?
STEM education is:
- Learning in each of the individual STEM subjects (science, technology and mathematics). Through developing deep knowledge in each of these disciplines, students build a foundation to identify and integrate connections between learning areas.
- Students draw knowledge from the disciplines of science, technology, engineering and mathematics to address a challenge or problem.
In our schools, students apply their knowledge of STEM to:
- test ideas
- take risks
- listen to and think about alternative ideas
- build knowledge that is applicable in real life.
Examples of STEM in action are:
- designing a greenhouse for the school garden
- working on an industry challenge
- formulating a solution to a local council problem.
Hands-on experience helps students to see the relevance and importance of studying STEM subjects. It also sparks students’ interest to explore STEM in fun and engaging ways. Watch this video to find out more.
Find out more about STEM learning
Why is STEM important?
Technology is rapidly reshaping our workforce. While some jobs will become less common, other interesting and new jobs will be created.
Workforce needs of the future
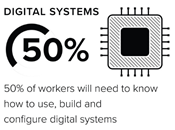



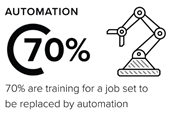

There will be more jobs that need non-routine thinking skills and high levels of originality and creativity. Studying and working in STEM means:
- learning about the world around us
- finding innovative solutions to real-world challenges
- playing a role in some of Australia’s major discoveries and developments.
Students who explore and develop 21st century skills and ways of thinking during school will be increasingly valued in the workplace. STEM offers a rich context for developing these skills and capabilities.
Watch this short video - students from Gladstone High School talk about STEM learning in the community.


